What is Spinal Stenosis:
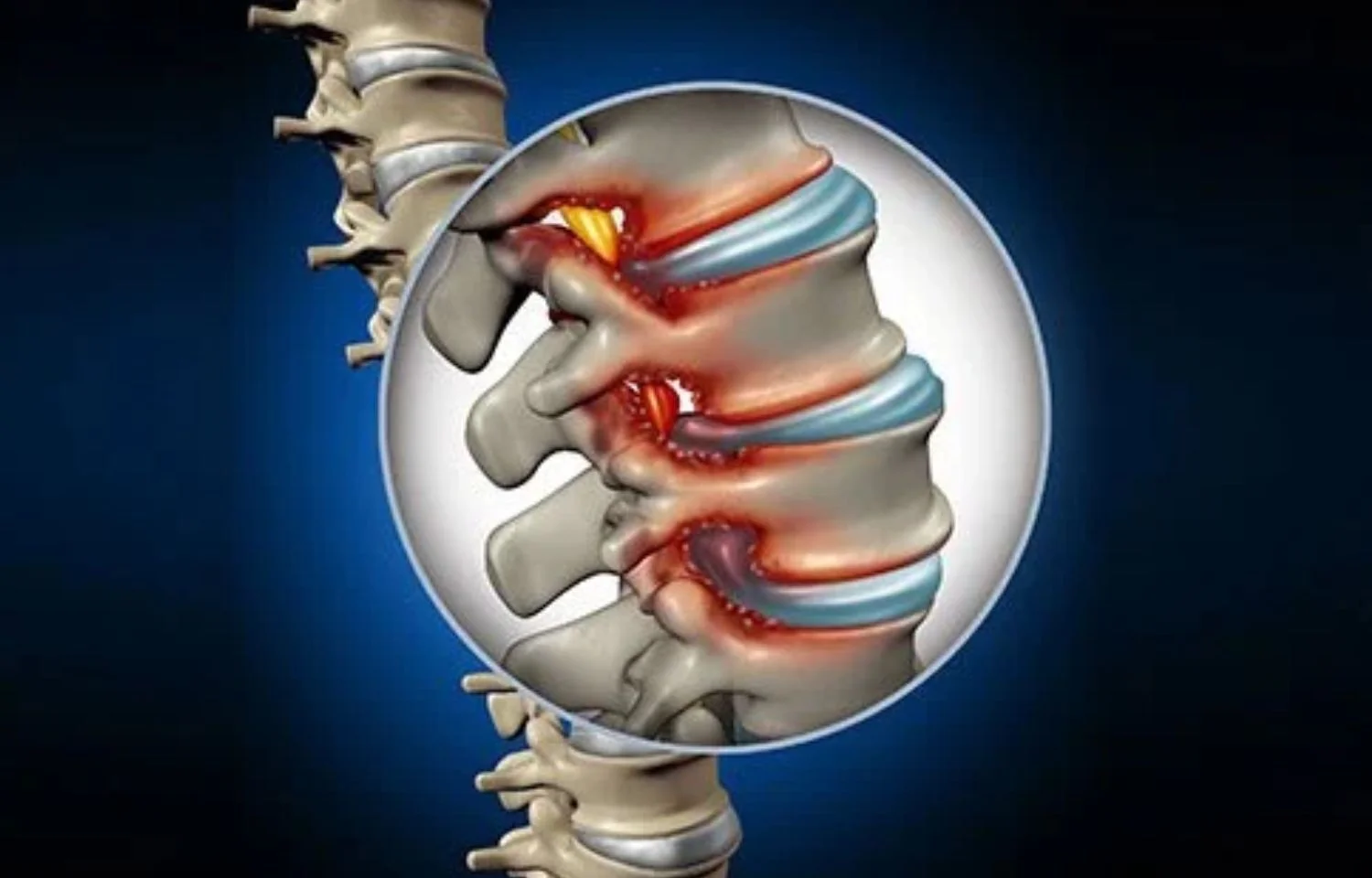
Spinal stenosis is a condition where the spinal canal, the space that houses the spinal cord and nerves, becomes narrowed. This narrowing can compress the spinal cord and nerves, leading to pain and other symptoms. The most common causes of spinal stenosis include:
- Degenerative Changes: As we age, the spine naturally degenerates. The discs between the vertebrae can lose height, and the joints can become arthritic, contributing to narrowing of the spinal canal.
- Herniated Discs: A herniated disc can bulge into the spinal canal and press on the spinal cord or nerves.
- Spinal Injuries: Trauma or injury to the spine can lead to stenosis.
- Genetic Factors: Some people may be born with a narrower spinal canal.
Symptoms of Spinal Stenosis?
- Lower Back Pain: Pain in the lower back that may radiate into the buttocks or legs.
- Leg Pain or Cramping: Pain, numbness, or weakness in the legs, which may worsen with walking or standing and improve with sitting or bending forward.
- Neck Pain: When stenosis occurs in the cervical spine (neck region), it can cause neck pain, arm pain, or weakness.
- Balance Issues: Difficulty walking or maintaining balance, especially in advanced cases.
How is Spinal Stenosis Diagnosed?
Diagnosis of spinal stenosis typically involves:
- Medical History and Physical Examination: Your doctor will review your symptoms and perform a physical exam to assess your spine and neurological function.
- Imaging Tests: MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) or CT (Computed Tomography) scans are commonly used to visualize the spinal canal and identify areas of narrowing and nerve compression.
- X-rays: Can help to identify changes in the spine’s structure, such as bone spurs or disc degeneration.
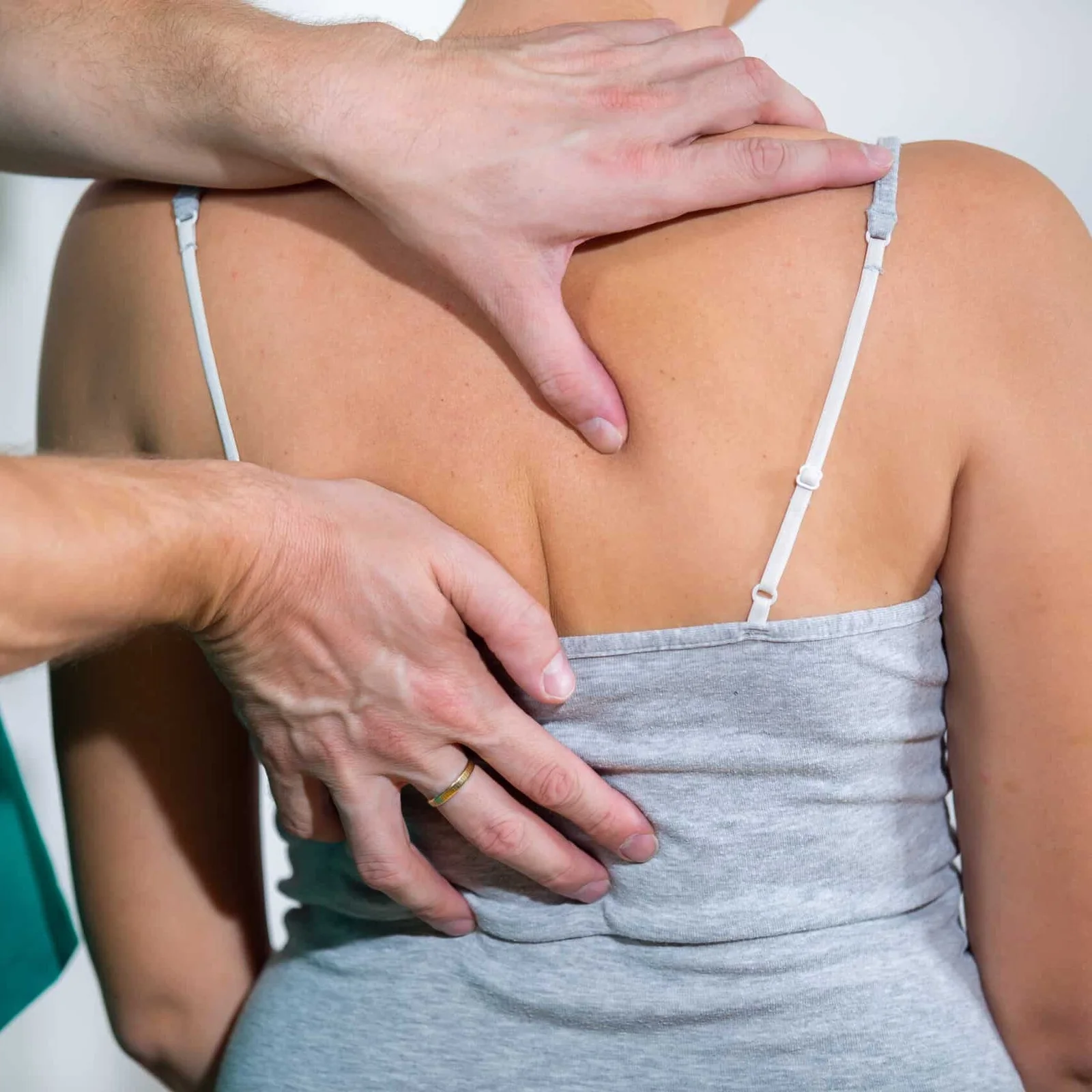
What Are the Treatment Options for Spinal Stenosis?
Treatment options for spinal stenosis aim to relieve symptoms and improve quality of life. They include:
- Conservative Treatments:
- Physical Therapy: Helps strengthen the muscles supporting the spine and improve flexibility.
- Medications: Pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs can help manage pain and reduce inflammation.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Weight management and activity adjustments can reduce stress on the spine.
- Interventional Procedures:
- Epidural Steroid Injections: These injections deliver anti-inflammatory medication directly into the spinal canal to relieve pain and reduce inflammation.
- Surgical Options:
- Decompression Surgery: Procedures such as laminectomy or foraminotomy can relieve pressure on the spinal cord or nerves by removing or trimming the structures causing the compression.
- Newer Treatment Options:
- Regenerative Medicine: Treatments such as Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) therapy or Stem Cell Therapy can help to promote healing and regeneration of damaged tissues in the spine.
- Vertiflex Procedure: This minimally invasive procedure involves implanting a small device to maintain space in the spinal canal and alleviate pressure on the nerves, particularly for patients who do not respond to more conservative treatments.
- Conservative Treatments:
