Neuropathic Pain
What is Neuropathic Pain and Its Symptoms?
Neuropathic pain is a type of chronic pain caused by damage or dysfunction in the nervous system. It can result from conditions such as diabetes (diabetic neuropathy), shingles (postherpetic neuralgia), spinal cord injuries, or nerve compression. Symptoms of neuropathic pain often include burning, tingling, stabbing, or shooting sensations, and the pain may be persistent or occur in episodes. It can also lead to heightened sensitivity to touch, known as allodynia, where even light contact causes significant pain.

How is Neuropathic Pain Diagnosed?
Diagnosing neuropathic pain begins with a thorough medical history and physical examination to identify underlying conditions that may contribute to nerve damage. Neurological tests help assess nerve function and sensitivity. Diagnostic tools such as nerve conduction studies, electromyography (EMG), and imaging studies like MRI may also be used to locate and evaluate nerve damage. Identifying the cause of neuropathic pain is essential for targeted treatment.
What is Neuropathic Pain and Its Symptoms?
Neuropathic pain is a type of chronic pain caused by damage or dysfunction in the nervous system. It can result from conditions such as diabetes (diabetic neuropathy), shingles (postherpetic neuralgia), spinal cord injuries, or nerve compression. Symptoms of neuropathic pain often include burning, tingling, stabbing, or shooting sensations, and the pain may be persistent or occur in episodes. It can also lead to heightened sensitivity to touch, known as allodynia, where even light contact causes significant pain.

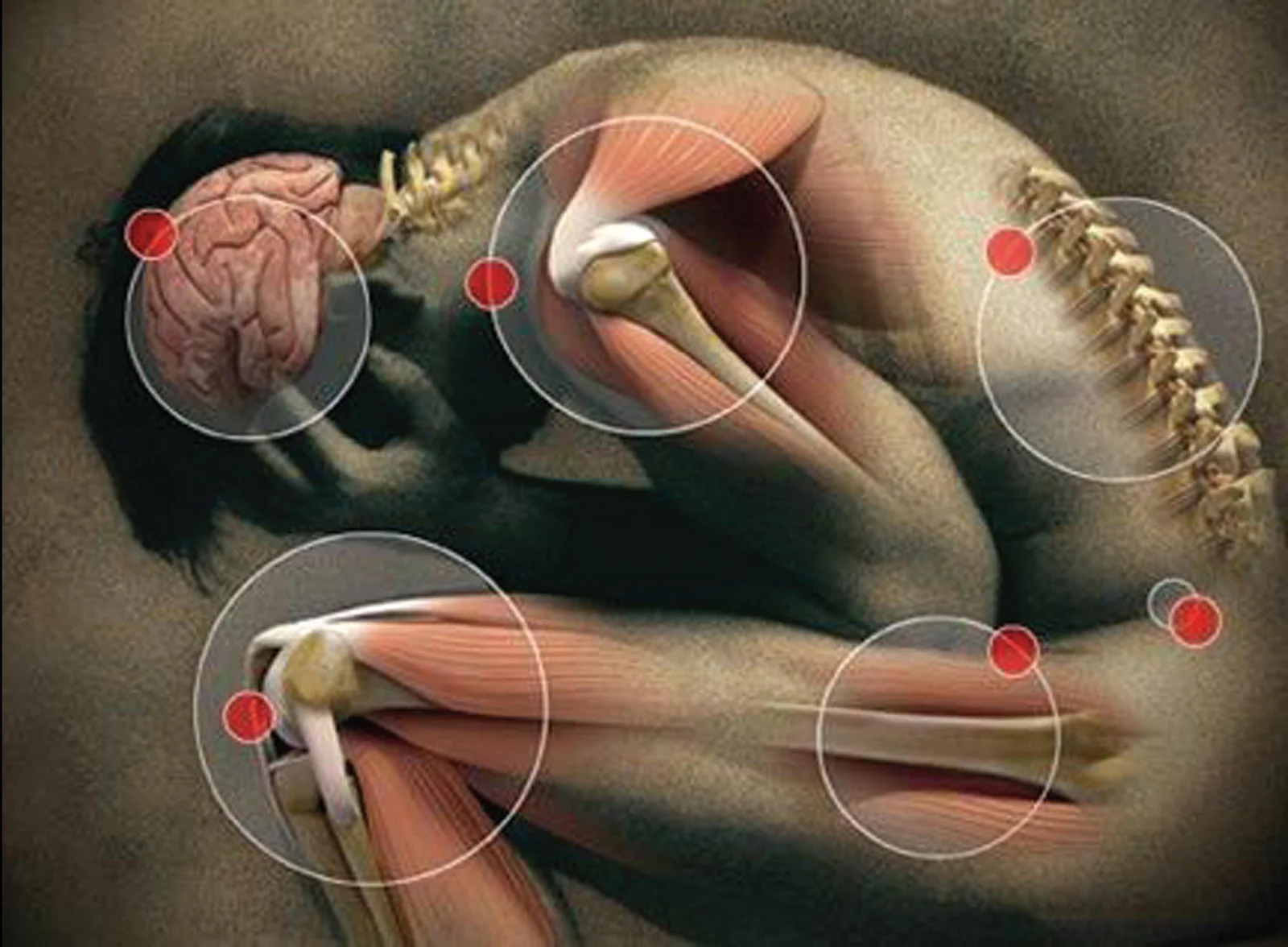
How is Neuropathic Pain Diagnosed?
Diagnosing neuropathic pain begins with a thorough medical history and physical examination to identify underlying conditions that may contribute to nerve damage. Neurological tests help assess nerve function and sensitivity. Diagnostic tools such as nerve conduction studies, electromyography (EMG), and imaging studies like MRI may also be used to locate and evaluate nerve damage. Identifying the cause of neuropathic pain is essential for targeted treatment.
